Description
Introduction
The Integrated Industrial Township in Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, represents a significant collaborative effort between India and Japan to foster industrial development and economic growth. Established under the broader framework of Japan Industrial Townships (JITs), the township aims to provide a robust infrastructure to attract Japanese businesses and support local economic activities. Despite its ambitious plans, as of December 2021, the township has not yet attracted any Japanese companies, highlighting both the potential and challenges faced by this initiative.
Historical Context and Development
In April 2015, the governments of India and Japan agreed to develop Japan Industrial Townships as part of the India-Japan Promotion Partnership announced in 2014. The primary objective was to create industrial clusters that would facilitate Japanese investments in India, thereby promoting economic collaboration and technological exchange between the two nations.
Location and Infrastructure
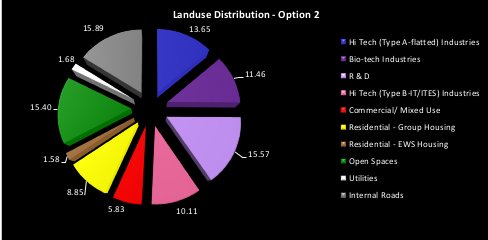
The Greater Noida Integrated Industrial Township (IIT) is strategically located in Uttar Pradesh, leveraging its proximity to major transportation hubs and markets. The township is designed to offer a range of facilities, including industrial plots, commercial spaces, residential areas, and social infrastructure. This integrated approach ensures that businesses have access to all necessary amenities, from power and water supply to housing and educational institutions.
Economic and Industrial Strategy
The township is intended to serve as a hub for various industries, particularly those with Japanese investment. The development strategy focuses on creating a conducive environment for businesses through streamlined administrative processes, such as single-window clearance systems, and robust infrastructure. The aim is to reduce bureaucratic hurdles and facilitate quicker establishment and operation of businesses.
Challenges and Current Status
Despite the well-laid plans, the Greater Noida IIT has faced challenges in attracting Japanese companies. As of December 2021, no Japanese companies had established operations in the township. This lack of traction can be attributed to several factors, including competitive industrial policies from other states, global economic conditions, and perhaps the need for more aggressive marketing and incentives to attract investors.
Comparative Analysis with Other JITs
When compared to other Japan Industrial Townships across India, the Greater Noida IIT's progress appears slower. For instance, Sri City in Andhra Pradesh hosts 25 Japanese companies, benefiting from its strategic location near ports and airports, robust infrastructure, and proactive state policies. Similarly, OneHub Chennai in Tamil Nadu and Mandal Industrial Park in Gujarat have successfully attracted multiple Japanese businesses by offering dedicated facilities and favorable business environments.
Social Infrastructure and Community Development
A critical aspect of the township's development plan includes social infrastructure to support the community. This includes residential areas, educational institutions, healthcare facilities, and recreational spaces. By providing a holistic living environment, the township aims to attract a skilled workforce and create a vibrant community.
Future Prospects and Recommendations
For the Greater Noida IIT to realize its full potential, several measures can be considered:
Enhanced Marketing and Outreach: More aggressive marketing strategies to promote the township to potential Japanese investors. This could involve roadshows, business delegations, and partnerships with Japanese trade organizations.
Incentive Schemes: Introduction of more attractive financial incentives, such as tax breaks, subsidies, and easier financing options for Japanese companies.
Improving Ease of Doing Business: Further simplification of administrative processes and reduction of bureaucratic red tape to make it easier for businesses to set up and operate.
Collaboration with Japanese Stakeholders: Strengthening ties with Japanese government bodies, industry associations, and businesses to better understand their needs and address any concerns.
Focus on High-Potential Sectors: Identifying and focusing on sectors that have high potential for Japanese investment, such as automotive, electronics, and precision engineering.
Conclusion
The Integrated Industrial Township in Greater Noida represents a significant opportunity for economic growth and industrial development in Uttar Pradesh. While the current status reflects certain challenges, the potential for success remains high if strategic measures are implemented. By learning from other successful JITs and tailoring its approach to meet the needs of Japanese investors, the Greater Noida IIT can become a key hub for Japanese businesses in India, fostering greater economic collaboration between the two nations.